Showing results 1-10 of 478 for cast
Search results
-
Tuesday, January 28, 2014
CAST’s Board of Directors named Lisa Poller and Gabrielle Rappolt-Schlichtmann as Co-Presidents of the nonprofit education research organization
-

Wednesday, January 10, 2018
CAST wins the 2017 New England Publishing Collaboration (NEPCo) Award for its role in the Understood partnership.
-

Monday, May 4, 2020
In a letter sent to each member of Congress, CAST CEO Linda Gerstle urged Congress to ensure that special education laws which provide for essential supports, services, instruction, and protections are upheld.
-

Customer Relationship Manager
Nathan Trites is the Customer Relationship Manager for CAST. He manages the Customer Relationship Management platform Salesforce and related tools in order to support CAST's data infrastructure.
-
Wednesday, July 17, 2019
CAST, in collaboration with Jobs for the Future and the Wisconsin Regional Training Partnership, is piloting an approach to documenting prior learning for persons with disabilities in the industrial maintenance technician apprenticeship pathway.
-
Wednesday, July 15, 2015
CAST Co-President Gabrielle Rappolt-Schlichtmann briefed members of Congress and Congressional staff at a breakfast meeting on Capitol Hill today on the work CAST is doing to improve education for students with dyslexia.
-
Thursday, January 25, 2018
Check out the responsive, accessible, flexible, brand new home for the UDL Guidelines!
-
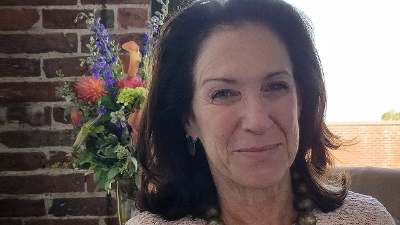
Wednesday, November 2, 2016
CAST's Board of Directors today announced the appointment of Linda Gerstle as the organization's Chief Executive Officer.
-
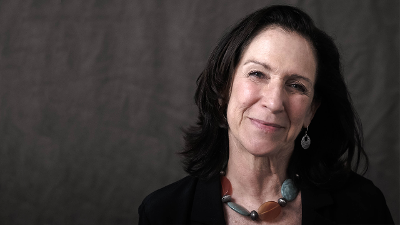
Saturday, February 20, 2021
Linda Gerstle, CAST's CEO, will retire on September 30, 2021. The planned transition will be coordinated over the next several months.
-
Wednesday, October 16, 2019
CAST released a statement after the U.S. House Education and Labor Committee introduced the College Affordability Act (H.R. 4674), which aims to improve opportunities for students from all backgrounds.
